What is a polymer? What are plastics?
Here is a simple explanation of the difference between polymers and plastics.
Is Plastic a Polymer?
All plastics are polymers, but not all polymers are plastic. Plastic is a specific type of polymer. Plastics are synthetic and do not occur naturally.
With this in mind, we can dig a little deeper into the definitions.
Differences between polymer and plastic?
The terms polymer and plastic are not the same. Plastic is a specific type of polymer comprised of a long chain of polymers. Polymers, on the other hand, are made up of uniform molecules that are smaller than plastic molecules.
What are polymers?
Polymers can be either natural or synthetic and are created when small molecules, also known as monomers, combine chemically to form a larger network of connected molecules. The term is derived from the Greek prefix “poly-,” which means “many,” and the suffix “-mer,” which means “parts.”
What makes these networks unique is the fact each polymer creates a network of repeating units. For example, a repeating unit in the chemical structure of natural rubber is isoprene. In the image below, you can see repeating units of isoprene after isoprene is turned into a natural rubber.
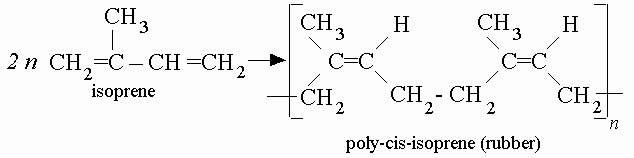
The repeating units in polymers are often carbon and hydrogen and sometimes oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, chlorine, fluorine, phosphorus and silicon.
Manufacturing with Plastics & Polymers
A lot of products now are being converted into plastic & polymer based materials due to cost-savings & efficiency benefits. If you are looking for a new manufacturing partner to help you develop your plastic product, contact us or head over to our plastic molding page for more details on our plastic molding services.
What is polymer plastic made of?
The most familiar plastic polymers including polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), epoxy and polyester (PS) are derived from petroleum hydrocarbons. These materials are used in a diverse range of applications. However, they do pose an end-of-life recycling and disposal issue as they do not break down easily. There is a big push to develop environmentally friendly polymers using biocomposites (also known as green composites) that are made up of biodegradable polymers including wood-derived polymers and non-wood fibers (straw, bast, leaf, seed, grass).
Natural Polymers Examples
The following are examples of natural polymers:
- Rubber
- Wool
- Protein
- Cotton
- DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
In fact, all life forms are made up of some combination of naturally occurring polymers.
What are plastics? How is Plastic Made?
Plastics are a specific type of synthetic polymer with a large molecular mass where the structure is mostly linear – they resemble spaghetti with long chains. The first synthetic plastic was created in 1909 for telephone and electrical components and was known as Bakelite.
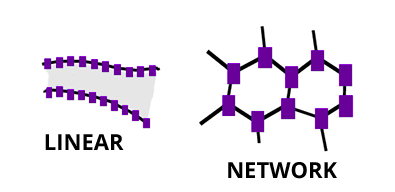
Manufactured polymers are called thermoset polymers when they are three-dimensional networks that do not melt once formed. An example would be an epoxy resin used in two-part adhesives.
What are Manufactured / Synthetic Thermoplastic Polymers?
Manufactured polymers are called thermoplastic polymers when they are one-dimensional chains that can be melted. The majority of manufactured polymers are thermoplastic, meaning they can be heated and reformed over and over again. This is the property that allows them to be recycled and reused.
Examples of synthetic thermoplastic polymers:
- PET (polyester) bottle / water bottle
- PE (polyethylene) film / plastic bags
- PS (polystyrene) cup / foam cup

Is polymer stronger than plastic?
All plastics are polymers but not all polymers are plastics. Plastic is a polymer typically made from oil and has a wide span of durability. Polymers can range in ‘strength’ from a bowling bowl to a grocery bag. Which is stronger? The answer is, it depends! How do you define strength and how do you compare two separate items with varying chemistry.
Polymer Characteristics
Each type of polymer has a very distinct characteristic, but here are some general attributes:
- Resistant to chemicals
- Thermal and electrical insulators
- Lightweight and strong
- Multiple process methods including extrusion, injection molded, blowmolded, etc.
- Petroleum based (typically but not always)
- Diverse and unique applications – plastics have changed the way we live, from medicine to automobiles to our homes
Negatives to Using Synthetic Polymers
While plastics have found an important role in our lives, there are several downsides:
- Made from nonrenewable crude oil resources
- Give off toxic fumes when burned
- Non-recyclable materials are difficult to re-purpose and do not decompose in landfills
To combat the end-of-use dilemma with this durable material, RSP uses a number of environmentally friendlier techniques. We incorporate recycled and reclaimed plastics from the ocean and use additives such as natural fibers from hemp and rice, as well as natural substances that help plastics biodegrade in landfills.
If you have additional questions or want to learn more about choosing the right material for your product, please contact us today!

